摘要: 为了实现高效的神经网络推理,我们希望通过最简单的网络实现最先进的准确性,同时尽量减少计算、内存和功耗的需求。网络量化到较低的精度是简化网络的一种强大技术。由于网络的每一层对量化的敏感性可能不同,混合精度量化方法选择性地调整各个层的精度,以实现任务性能(例如,准确性)的最小下降。为了估计层精度选择对任务性能的影响,本文介绍了两种方法:i) 基于熵近似指导的层选择(EAGL)方法快速且使用权重分布的熵;ii) 精度感知层精度选择(ALPS)方法直接且依赖于降低层精度后的单轮次微调。通过使用EAGL和ALPS进行层精度选择,对于ResNet-50、ResNet-101和BERT-base变换器网络,通过混合4位和2位层,恢复了全精度的准确性,整个准确性-吞吐量前沿展示了提升的性能。这些技术比几个相当的比较中现有的技术展现了更好的性能。值得注意的是,这是通过显著减少达到解决方案所需的计算时间来实现的。
1. Intro
当前做混合精度模型量化的计算成本太高了,需要有一种方法能够低成本地选择每一层的精度,更重要的是能够低成本且准确的估计这种精度的选择对模型表现的评估。
本文提出Accuracy-aware Layer Precision Selection(ALPS)和Entropy Approximation Guided Layer selection(EAGL),并通过结合上述两种手段设计了一个能进行2bit-4bit混合精度量化的框架,在ResNet50/101和BERT-base的网络上做了实验。
- ALPS: 考虑一个网络,要评估一层的量化后的影响,最简单的方法就是先把精度-1,然后fine-tune一个epoch,然后看模型的精度变化大不大。这种方法需要假设每一层之间的贡献都是独立的。只要逐层做这样的量化,当精度下降多的时候就不-1,精度下降少就-1然后重复,就能完成对整个网络的量化。
- EAGL: 假设保持了合适的正则化的情况下,一个已经训练好. dth应该和这一层实际需要的bit width差不多(因为只能表达这么多信息),那么假设有一个已经训练好的模型,只需要估计每一个layer的参数经验分布的熵就能判断对应的layer需要的bit width。这种操作不需要重复测试模型精度也不需要考虑训练集中的数据规模。
文章中的精度只考虑4bit和2bit,可能是因为他们是NorthPole团队的,只做了加速器上支持的两种精度。
Contribution:
- Two elegant measures for estimating the impact of layer precision on task performance that achieve SOTA results for mixed precision NN
- A framework for fair comparison across varying approaches that decomposes the bit-width configuration selection problem into three steps: accuracy gain estimation, layer-wise precision selection for a budget using 0-1 Integer Knapsack optimization algorithm, and fine-tuning of resulting mixed precision network.
2. Related Work
AutoQ等基于RL的,HAWQ系基于Hessian的,还有一种受到few-shot方法启发的基于“imprinting”的方法的,但是需要修改原始网络的结构。目前SOTA还是HAWQ-v3。
3. Methods
Mixed precision quantization is based on the intuition that different layers in a network have different sensitivity to quantization and hence some layers are better candidates for more aggressive quantization than others.
3.1. Evaluation Methodology
Maximize,while keeping 。是每一层选择更高bit width(文中是4bit)相比低精度(文中是2bit)带来的精度提升,是mask,选高bit为1低bit为0; 是对应layer的computational cost, 是总computational budget。
变成一个01背包问题。所以多个不同精度的选择可以认为是一个多重背包问题?
3.2. Accuracy-aware Layer Precision Selection for quantization (ALPS)
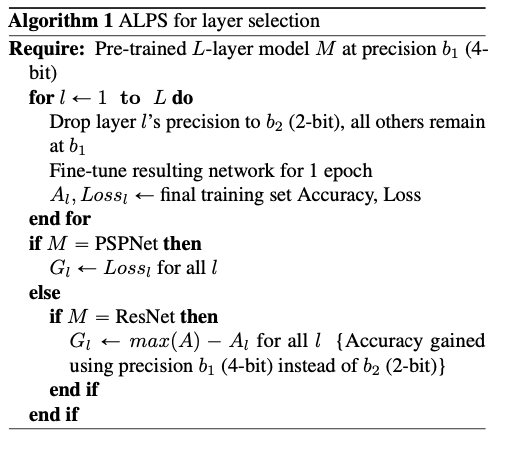
The intuition is that layers that have the highest accuracy gain when quantized to a higher precision b1 (here, 4-bit) instead of a lower precision b2 (here, 2-bit) are good candidates to be kept at b1 in a mixed precision network.
大致逻辑是先从最高的精度开始训练,然后一次将一层的精度降低2bit,训练一个epoch,测一下精度,观察精度的变化。
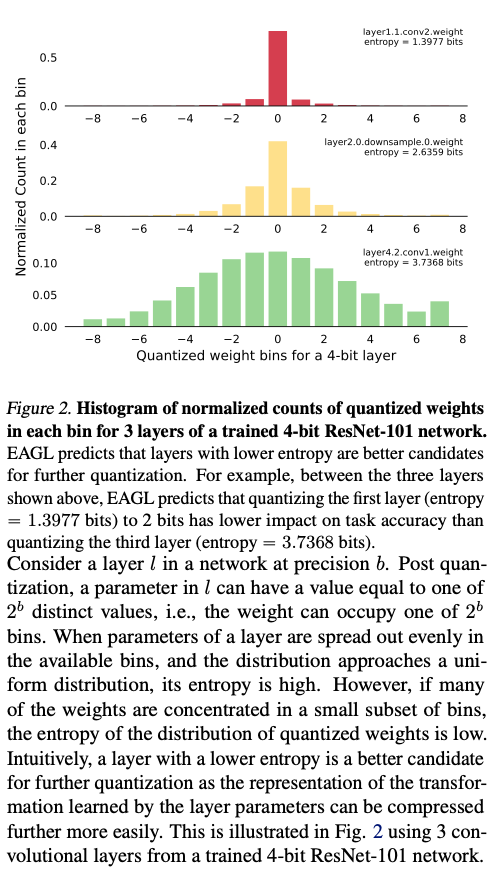
3.3. Entropy Approximation Guided Layer selection for quantization (EAGL)
设:
是层的个常数,被量化到上,当时为1,否则为0。

通过统计一个训练好的模型每一层的经验熵H,评估该层需要使用的量化精度。
3.4. Implementation details
3.4.1. Setting Layer Precision
如果activation会输入到多个layer中,这些layer必须是相同精度的。第一层和最后一层固定到8bit
3.4.2. Training And Implementation Details
在ResNet50, ResNet101, BERT, PSNet上做测试,对多个不同的计算资源budget做了测试
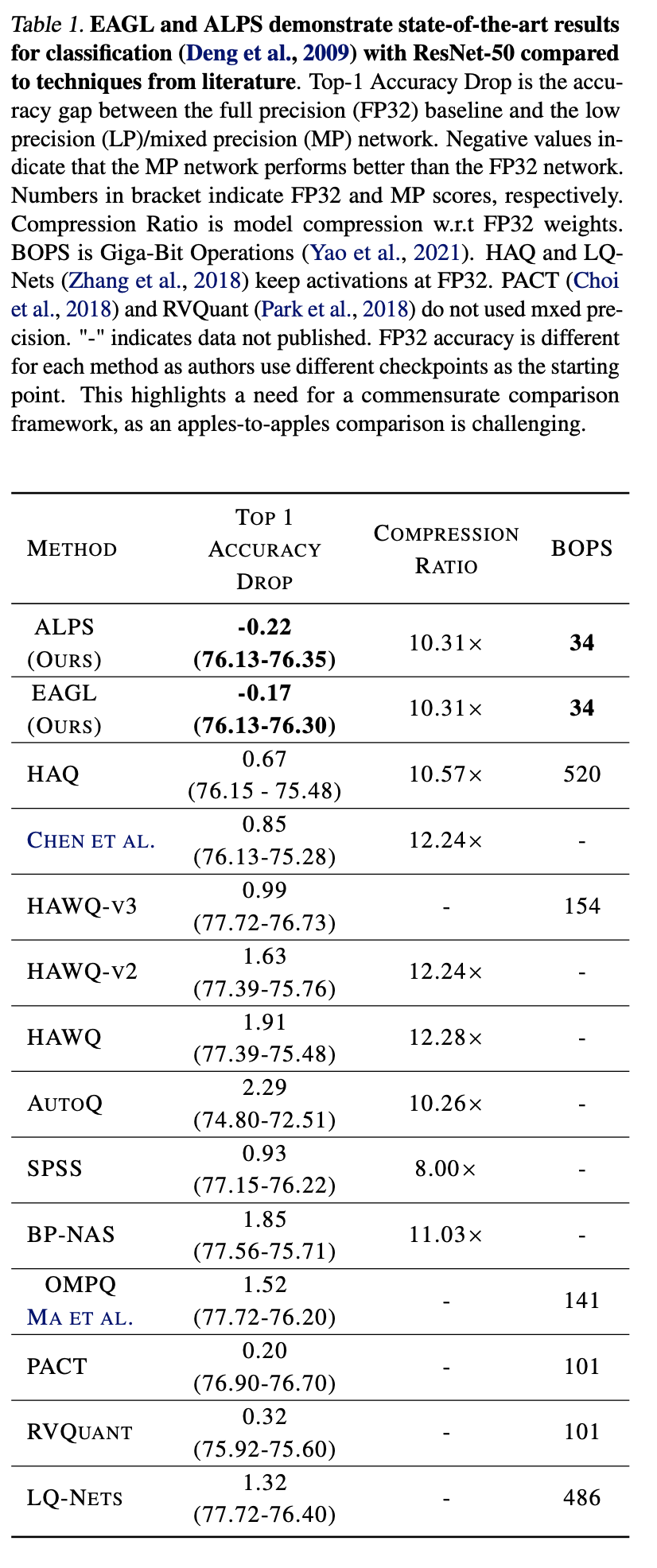
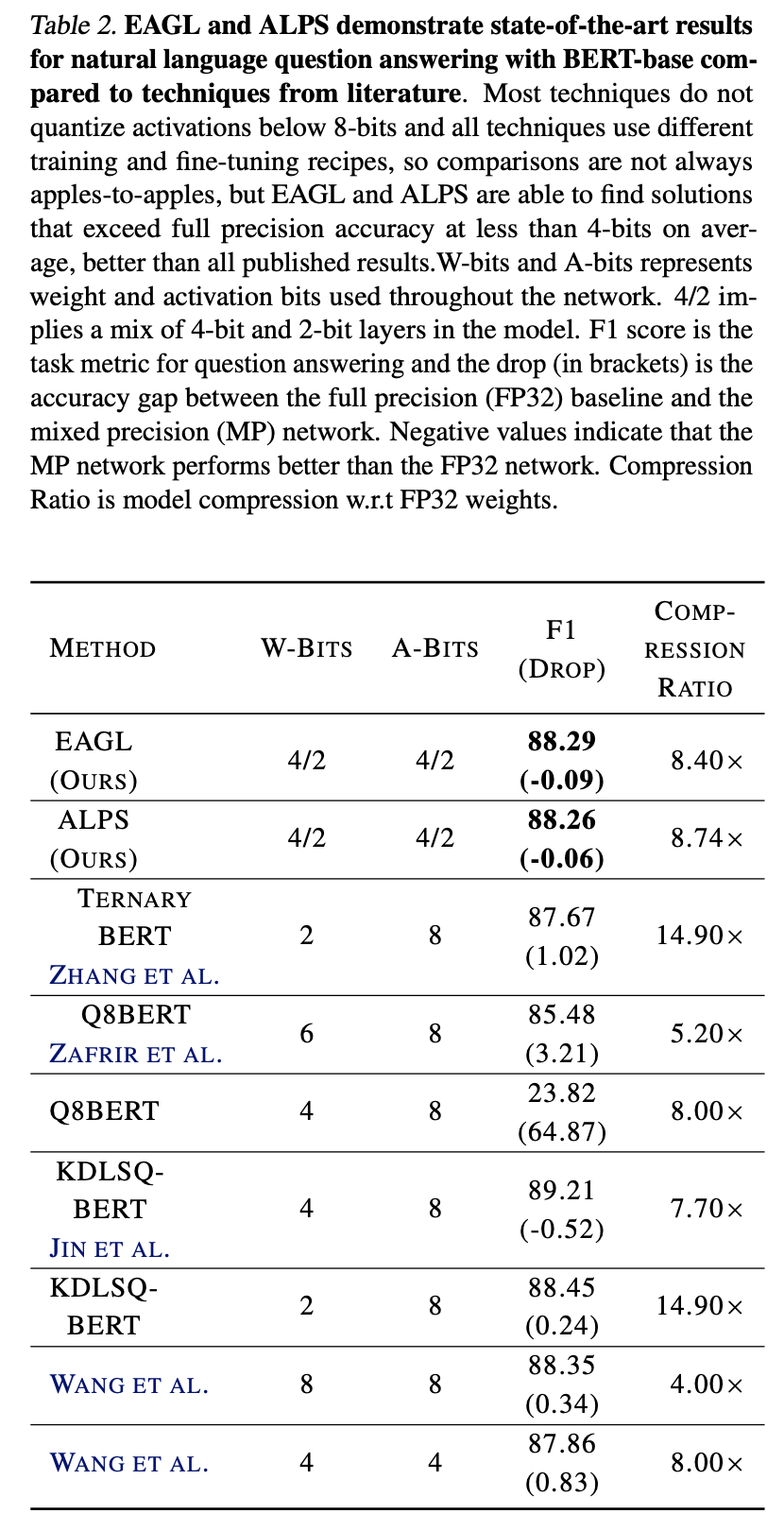
4. Results
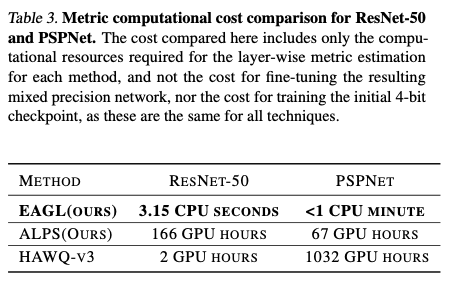
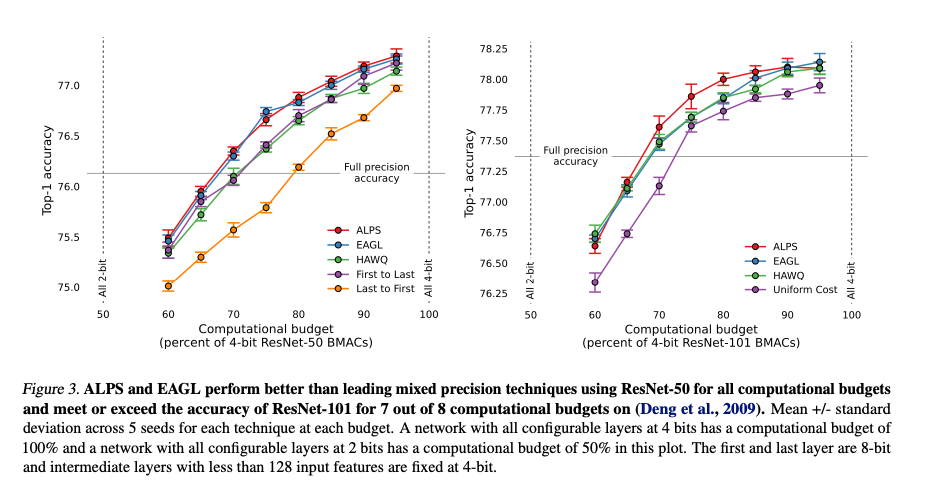
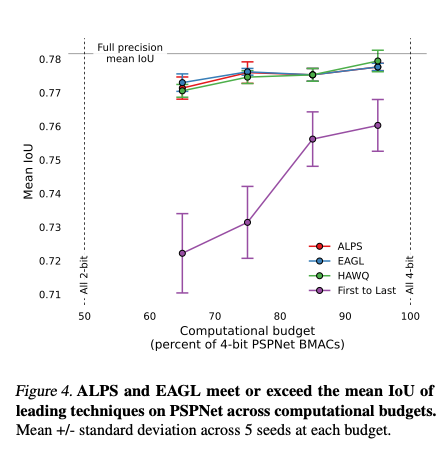
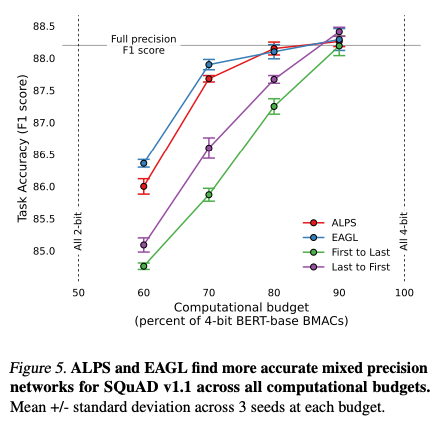
5. Conclusion
两种新的方法,主要目标都是减少计算资源的需求的情况下做量化。但是只考虑了2bit和4bit,并且实验和方法设计看起来都有点可疑。比如一个layer内的常数的分布范围并不能完全体现layer包含的信息,考虑一个layer的值全部都是2或者3,虽然只看分布可以量化到同一个bit上,但是实际上这个分布本身的偏移也包含了信息。可能是没有看懂文章具体是怎么处理这些内容的。